F(x) = P(X x) = Z x 1 f(t) dt;
”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã-IBFI = IAEI ICEI = 21AEI lAC!22 3 Continuous Functions If c ∈ A is an accumulation point of A, then continuity of f at c is equivalent to the condition that lim x!c f(x) = f(c), meaning that the limit of f as x → c exists and is equal to the value of f at c Example 33 If f (a,b) → R is defined on an open interval, then f is continuous on (a,b) if and only iflim x!c f(x) = f(c) for every a < c < b
”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ãのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  | |
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
:format(jpeg):mode_rgb():quality(40)/discogs-images/R-2261719-1540628439-9380.jpeg.jpg) |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
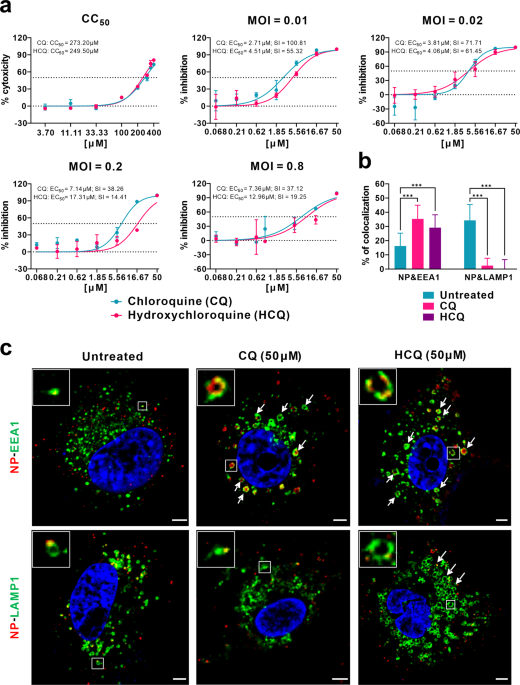 |  | |
 | ||
 | ||
「”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX ƒ{ƒu 30‘ã」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 | ||
.jpg) | 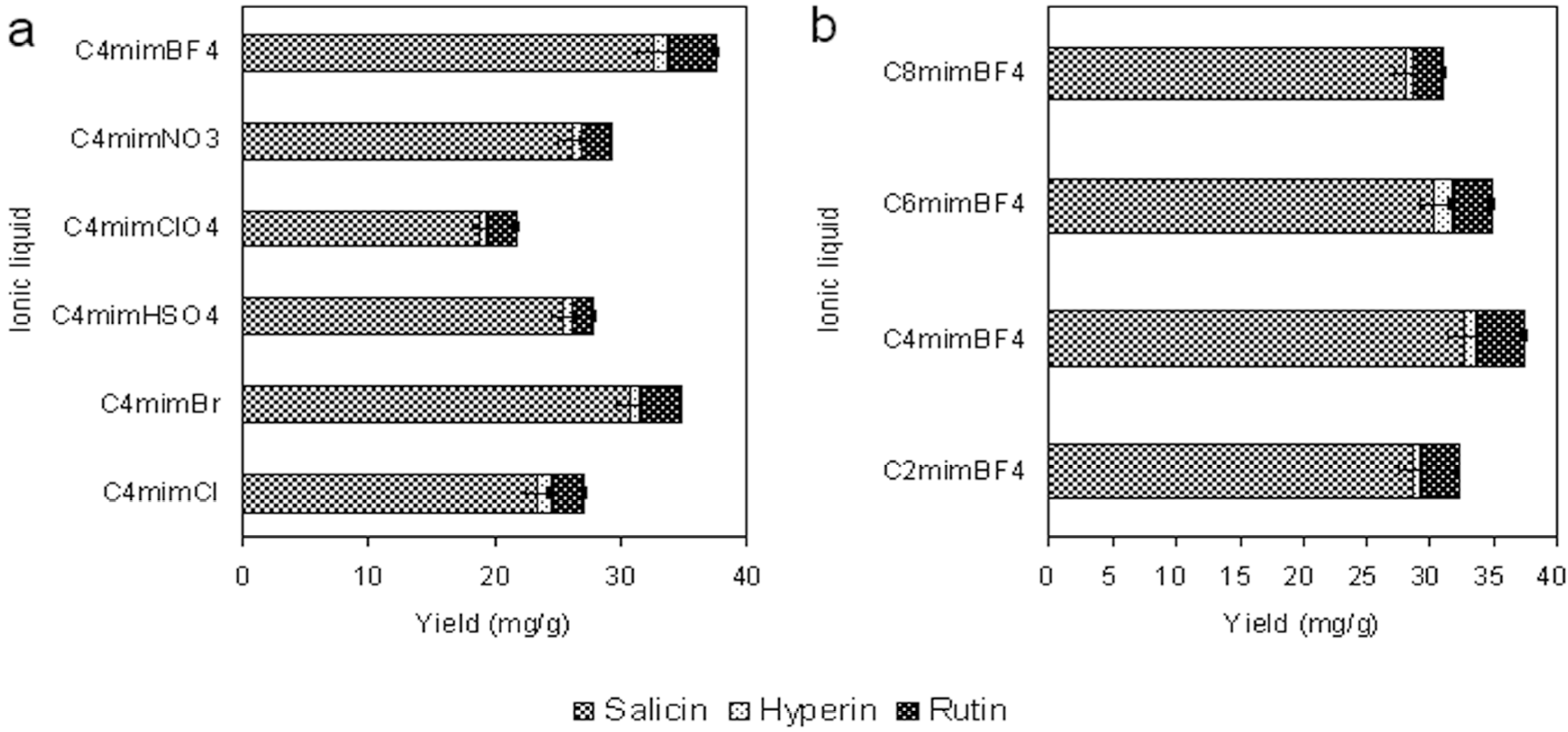 |
A function from a set X to a set Y is an assignment of an element of Y to each element of XThe set X is called the domain of the function and the set Y is called the codomain of the function A function, its domain, and its codomain, are declared by the notation f X→Y, and the value of a function f at an element x of X, denoted by f(x), is called the image of x under f, or the value of fF(x) is continuous on an interval a,b, and f(a)f(b)





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿